- Home
- A-Z Catalogue
- Products
- Valves
- Cetop
- Manual Directional Valves
- Proportional Valves
- Poppet Valves
- High-Speed Linear Servo Valves
- All High-Speed Linear Servo Valves
- Cetop 10 (NG32) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-10
- Cetop 10 (NG32) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-10 (With Fail-Safe)
- Cetop 8 (NG25) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-06
- Cetop 8 (NG25) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-06 (With Fail-Safe)
- Cetop 7 (NG16) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-04
- Cetop 7 (NG16) Two Stage Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVHG-04 (With Fail-Safe)
- Cetop 5 (NG10) Direct Type High Speed Linear Servo Valves – LSVG-03
- Cetop 5 (NG10) OBE Type Direct Operated Linear Servo Valves – LSVG-03-EH
- Cetop 3 (NG6) OBE Type Direct Operated Linear Servo Valves – LSVG-01-EH
- Pumps
- Pressure control
- Flow Control Valves
- Pressure Control Valves
- All Pressure Control Valves
- Brake Valves
- Direct Relief Valve
- Low Noise Solenoid Controlled Relief Valves
- Low Noise Pilot Operated Relief Valves
- Pilot Operated Relief Valves
- Pressure reducing and relieving valves
- Pressure reducing and check valves
- Pressure control valves
- Remote Control Relief Valves
- Solenoid Controlled Relief Valves – BSG
- Solenoid Controlled Relief Valves – BST
- Unloading relief valves
- Check valves
- Environmental
- Valves
- Hydraulic Systems
- Power pack
- About Us
- Contact
- Blog
What is a Directional Valve and How Does It Work?
A directional valve is a crucial component in many hydraulic and pneumatic systems. It controls the flow path of fluids, allowing operators to direct movement. Understanding how a directional valve works can enhance the efficiency of various machinery. These valves are characterized by ports and positions, which, though straightforward, can be complex in different applications.
In practice, a directional valve's precise functioning can determine machine performance. While some may think of it as merely a switch, it influences everything. Misalignments or failures in a directional valve may result in operational inefficiencies. It's not uncommon to encounter problems that require thoughtful evaluation. The challenge often lies in ensuring the valve responds accurately under pressure, rather than just assuming it will.
Ultimately, grasping the role of a directional valve can lead to more effective machinery management. Understanding its mechanics invites a deeper reflection on maintenance and design. The interactions within these systems offer insights that can be both enlightening and perplexing. By exploring the nuances of directional valves, one can appreciate their importance in everyday applications.
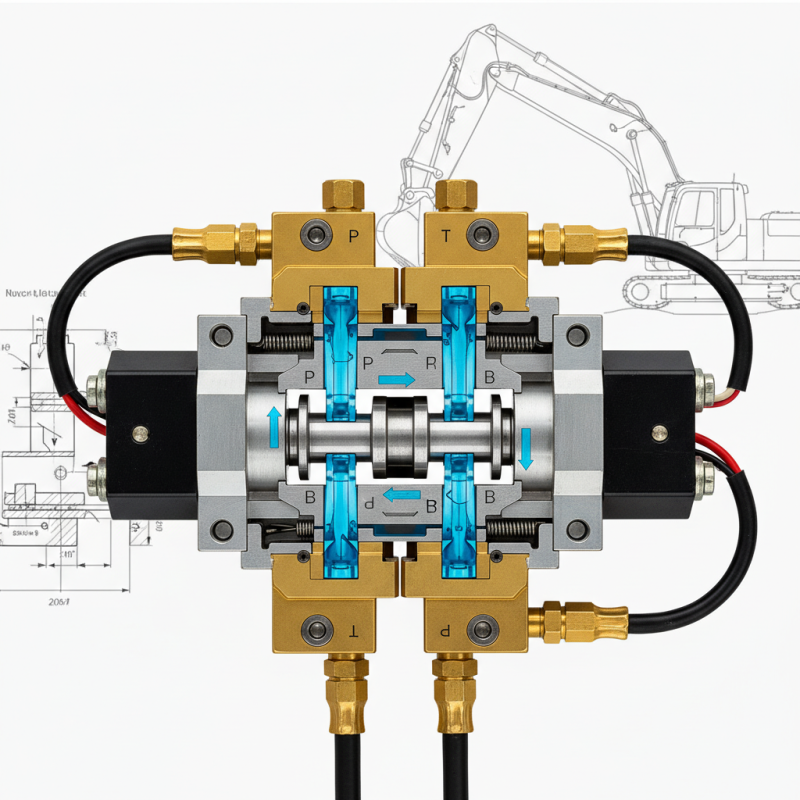
Table of Contents
[Hide]
What is a Directional Valve?
A directional valve is a key component in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. It controls the flow direction of fluids or gases. These valves help shape the movement and operation of machines. By managing how fluid moves, they ensure systems operate smoothly.
Most directional valves have multiple ports. They can either open or block paths for the fluid. Common configurations include two-way, three-way, and four-way. Each design serves a unique purpose. In fact, industry reports suggest that directional valves make up about 30% of the total hydraulic valve market. This highlights their critical role in automation.
Tips: Regular maintenance is essential. Check for leaks and ensure proper function. Ignoring these checks can lead to costly repairs. Keep an eye on pressure levels; fluctuations can indicate problems.
In some cases, operators may face challenges. For instance, a valve may stick or fail to operate as intended. This could be due to dirt accumulation or wear over time. If this happens, immediate assessment is crucial. Understanding the cause helps prevent system failures later on. Always document any issues for future reference.
Directional Valve Performance Data
Types of Directional Valves
Directional valves are essential components in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. They control the flow of fluid by directing it to different paths. Different types of directional valves serve specific functions and applications.
One common type is the spool valve. It uses a sliding spool to open and close passages. Spool valves can be manually operated, solenoid controlled, or actuated by hydraulic pressure. Another type is the poppet valve. These valves utilize a ball or cone that seats against a surface to stop the flow. Poppet valves are often found in systems requiring a tight seal.
Additionally, there are rotary valves, which provide flow direction through rotation. These valves typically manage higher flow rates and can be more compact. Each type has its pros and cons. For instance, spool valves can be versatile but may leak over time. Poppet valves are reliable yet may require more precise alignment. Understanding these types helps in selecting the right directional valve for specific needs.
What is a Directional Valve and How Does It Work? - Types of Directional Valves
| Type | Actuation Method | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solenoid Valves | Electromagnetic | Industrial Automation | Fast switching, compact size | High power consumption |
| Pneumatic Valves | Pneumatic Actuator | Robotics, Packaging | Suitable for high-speed applications | Requires compressed air supply |
| Hydraulic Valves | Hydraulic Actuator | Heavy Machinery | High force output | Potential for leaks |
| Manual Valves | Manual Control | Maintenance Tasks | Cost-effective, no power needed | Slower response time |
How Directional Valves Function
Directional valves are essential components in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. They control the flow direction of fluids. By doing so, they enable systems to perform tasks with precision. Research indicates that the global directional control valve market size was valued at over $3 billion in 2020, with a projection to grow by 6% annually through 2027.
These valves operate using a spool that moves within a cylinder. When the spool shifts, it opens or closes ports. This movement directs fluid to different parts of the system. For example, in a hydraulic press, the valve helps control the movement of the ram. However, improper handling can lead to system inefficiencies. Operators must understand the valve's specifications to prevent issues such as leaks or malfunction. In 2022, about 15% of hydraulic failures were linked to inadequate valve maintenance, emphasizing the need for regular checks.
In practice, the setup may seem straightforward. Yet, environmental factors, such as temperature and contamination, can affect functionality. Even slight deviations in a valve’s tolerance can lead to significant performance drops. A notable study found that 20% of operational downtime in manufacturing is caused by hydraulic system failures, frequently tied to directional valve issues. Ongoing training for technicians on these systems can mitigate many problems.
Applications of Directional Valves in Industries
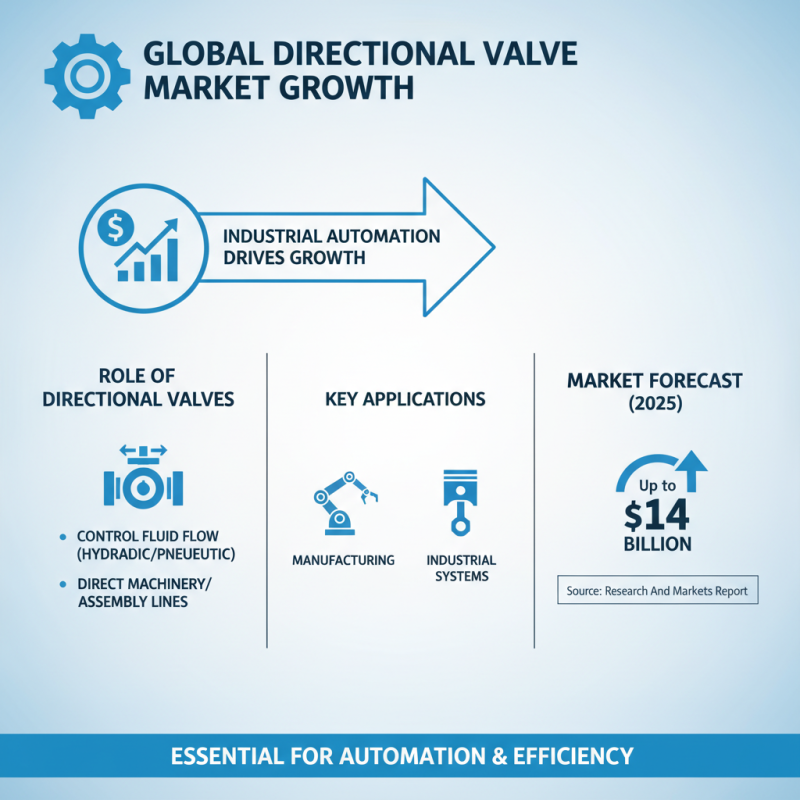
Directional valves play a crucial role in various industrial applications. They control the flow of fluids in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. In manufacturing, for example, they direct the movement of machinery and assembly lines. A report by Research And Markets indicates that the global directional valve market will grow to around $14 billion by 2025. This growth reflects the increasing reliance on automation in industries.
In the automotive sector, directional valves are vital in braking systems and power steering. They enhance safety and efficiency in vehicle design. According to a 2022 study by Technavio, the automotive industry accounts for approximately 30% of the market. However, the complexity of these systems can lead to maintenance challenges. Improper installation or malfunction can create significant downtime.
Moreover, in the construction sector, directional valves are essential for operating heavy equipment. They manage hydraulic cylinders and motors, enabling precise control. Yet, users must be aware of the potential for failure. A minor error in valve selection or installation can lead to operational inefficiencies. Continuous improvement and training are necessary to ensure reliability in these critical applications.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Directional Valves

Directional valves play a crucial role in hydraulic systems. Their maintenance is essential to ensure longevity and optimal performance. According to industry reports, nearly 20% of hydraulic failures are linked to valve issues. Regular inspection and timely maintenance can prevent such failures. Visual checks for leaks or unusual noises during operation can provide early indicators of a problem.
Troubleshooting directional valves often starts with identifying the symptoms. Uneven flow or pressure drops could indicate a blockage. Cleaning screens and replacing filters regularly can minimize these risks. The average cost of valve replacement can range from $500 to $2,000, making preventive maintenance a cost-effective alternative. Neglecting small signs can lead to complete system failures, requiring extensive repairs. Operators should be cautious and proactive.
Consideration should be given to fluid quality as well. Contaminated fluid can cause wear and tear on valve components. Additionally, hydraulic fluid should be checked regularly. This ensures proper viscosity and performance levels. Inadequate maintenance practices reflect poorly on operational efficiency. Proper training and awareness can make a significant difference in valve lifespan and system reliability.
Related Posts
-

The Essential Guide to Understanding Pressure Relief Valves: Safety and Function Explained
-
The Essential Guide to Understanding Hydraulic Power Packs in Industrial Applications
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Pressure Reducing Valve
-

Top 10 Yuken Valve Solutions for Optimal Hydraulic Performance
-
2025 Top 5 Proportional Valves to Enhance Your Industrial Efficiency
-

What is a Pilot Operated Check Valve and How Does It Work in Hydraulic Systems












